
Concentration of chloride ion = 5.5M not the unit activity of 1M.The reactants may be in nonstandard conditions which means that the voltage for the half cells may be less or more than the standard condition amount.There might be more than one electrode reaction that occurs meaning that there may be more than one half-reaction leaving two or more possibilities for the cell reaction.H 2 (g) requires a 1.5 V overpotential, while Pt (s) requires 0 V overpotential This case happens more frequently with gases. An overpotential or voltage excess is sometimes needed to overcome interactions at the electrode surface.There are four primary factors that determine whether or not electrolysis will take place even if the external voltage exceeds the calculated amount: If an aqueous solution of sodium chloride were used in the above system, hydrogen would undergo reduction instead of sodium, because it is a stronger oxidizing agent that sodium.

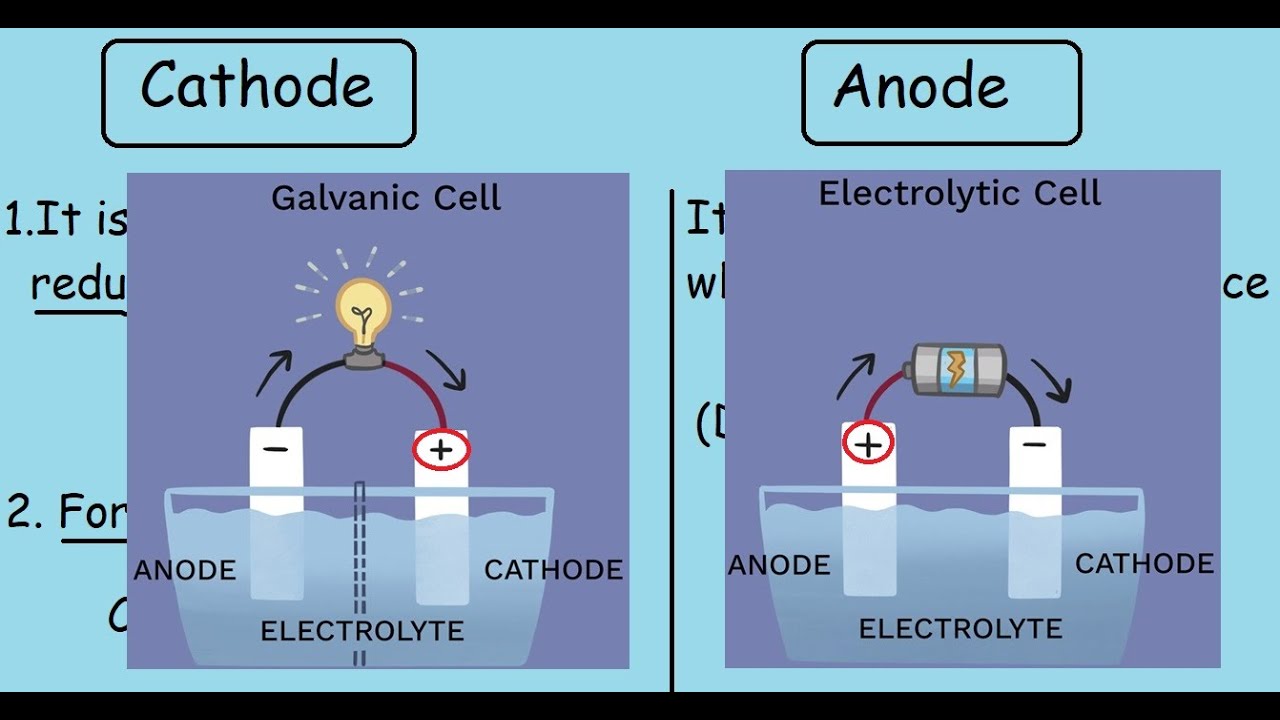
The substance that is the strongest oxidizing agent will be reduced. The substance that is the strongest reducing agent (the substance with the highest standard cell potential value in the table) will undergo oxidation. The conditions under which the electrolyte cell operates are very important.Anode is now positive charged and the cathode has a negative charged. Note that the site of oxidation is still the anode and the site of reduction is still the cathode, but the charge on these two electrodes are reversed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
